Integral
Integration ist die umgekehrte Operation der Ableitung.
Das Integral einer Funktion ist der Bereich unter dem Funktionsgraphen.
Unbestimmte integrale Definition
Wann
![]()
Unbestimmte integrale Eigenschaften
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Änderung der Integrationsvariablen
Wann
![]() und
und
![]()
![]()
Integration in Teilstücken
![]()
Integraltabelle
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definitive integrale Definition
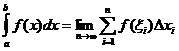
Wann
![]()
![]()
![]()
Definitive Integralberechnung
Wann
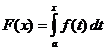 ,
,
![]()
![]() und
und
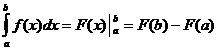
Bestimmte integrale Eigenschaften
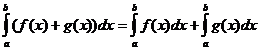
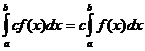
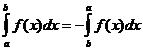
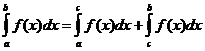
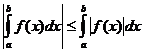
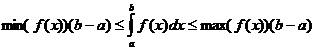 wann
wann
![]()
Änderung der Integrationsvariablen
Wann
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]()
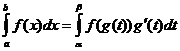
Integration in Teilstücken
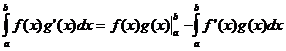
Mittelwertsatz
Wenn f ( x ) stetig ist, gibt es einen Punkt
![]() damit
damit
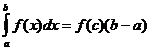
Trapezförmige Approximation eines bestimmten Integrals
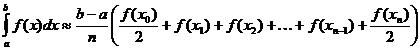
Die Gammafunktion
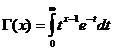
Die Gamma-Funktion ist konvergent für x/ 0 .
Eigenschaften der Gammafunktion
G ( x + 1) = x G ( x )
G ( n + 1) = n ! , wenn n ℕ (positive ganze Zahl).
![]()
Die Beta-Funktion
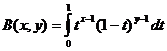
Beta-Funktion und Gammafunktionsbeziehung
INFINITESIMALRECHNUNG
- Grenze
- Derivat
- Integral
- Serie
- Laplace-Transformation
- Faltung
- Kalkülsymbole