Integral
La integración es la operación inversa de la derivación.
La integral de una función es el área debajo de la gráfica de la función.
Definición integral indefinida
Cuando
![]()
Propiedades integrales indefinidas
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Variable de cambio de integración
Cuando
![]() y
y
![]()
![]()
Integración por partes
![]()
Tabla de integrales
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definición integral definida
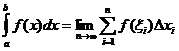
Cuando
![]()
![]()
![]()
Cálculo integral definido
Cuando
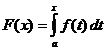 ,
,
![]()
![]() y
y
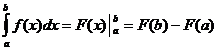
Propiedades integrales definidas
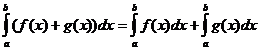
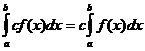
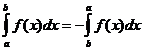
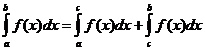
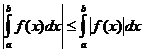
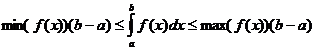 cuando
cuando
![]()
Variable de cambio de integración
Cuando
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]()
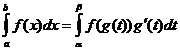
Integración por partes
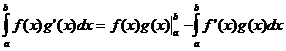
Teorema del valor medio
Cuando f ( x ) es continua hay un punto
![]() entonces
entonces
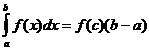
Aproximación trapezoidal de la integral definida
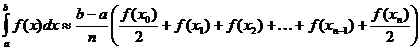
La función gamma
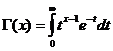
La función Gamma es convergente para x/ 0 .
Propiedades de la función gamma
G ( x +1) = x G ( x )
G ( n +1) = n ! , cuando n ℕ (entero positivo).
![]()
La función beta
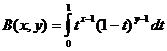
Relación función beta y función gamma